Rotation around the C-C bond in ethane
The simplest n-alkane is ethane, C2H6. The
bond between the two carbon atoms is a single ('sigma') bond, that is
rotation symmetric with respect to the C-C axis, so it allows rotation
around this axis. When rotating around this carbon-carbon bond, the energy of
ethane varies because of the presence of the C-H bonds.
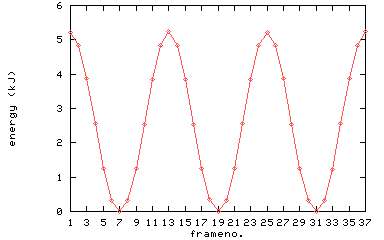
Have a look at
the energy as a function of the rotation around the carbon-carbon bond in
ethane. Such a plot you will also find in your textbook.
|
Use these animation control buttons, or click on a point in the graph.
|
|
|
|
Energies are from AM1 calculations and are for qualitative discussion only. Better calculations would give different quantitative results. This page was adapted by Bob Hanson for Internet Explorer 4 and Netscape 7 from the original, written by Hens Borkent