The
Total Synthesis of (+)-Discodermolide
Reviewed by Elizabeth Adams, Brett Aplin and Cory Paterson
Department of Chemistry, St. Olaf College, Northfield, Minnesota
Reviewed December 11, 2001
Discodermolide originally isolated from the sponge, discodermia dissoluta, the marine natural product (+)-discodermolide, has strong immunosuppressive activity. It acts as an anticancer agent reducing tumors. It inhibits cellar proliferation in the G2 and M phases of mitosis and also is know to stabilize microtubules. In a wide range of human cells, (+)-discodermolide causes mitotic arrest at metaphase-anaphase transition by stabilizing the microtubules that form at the centromeric poles.
Discussion:
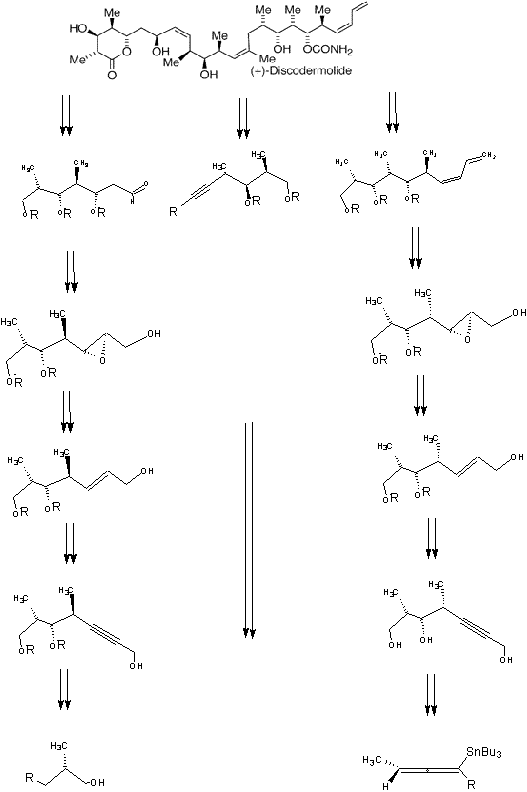
The main purpose of this investigation was to assemble the subunits of the polypropionate immunosuppressive agent (+)-discodermolide. This highly active natural product has been the target molecule for many synthetic studies. This particular study hopes to synthesize the three fragments of this homochiral compound, (+)-Discodermolide. In this approach, key stereocenters are introduced through additions of chiral allenylmetal reagents to the readily available aldehyde (S)-2-metheyl-3-silyoxypropanal. Subsequent reduction of the triple bond in regioselective expoxide cleavage with hydride or methyl cuprate provides the subunits of (+)-discodermolide. (+)-Discodermolide is a competitive inhibitor for the mitotic cycle. This study uses Sharpless epoxidation because it insures a selective oxidation in synthesis, providing a homochiral compounds or a nonracemic mixture. Thus, it’s an asymmetric epoxidation. The two separate schemes the researchers came up with allow this to happen. Each scheme creates a subunit of the compound having separate chiralities. One scheme is comprised of a certain segment of the product with a different chirality than the second scheme. The Sharpless Epoxidation was used for each scheme because it helps create specific stereochemistry. The epoxide stereochemistry as stated earlier produces a high yield of a non-racemic mixture thus the product remains uncontaminated.
Retrosynthetic Scheme
Works Cited:
Hung, Deborah T. Chen, Jie. Schreiber, Stuart L. “(+)-Discodermolide Binds to Microtubules in Stoichiometric Ratio to Tubulin Dimers, Blocks Taxol Binding and Results in Mitotic Arrest.” Chemistry & Biology 3 (1996): 287-293.
Marshall, James A. Johns, Brian A. Lu, Zhi-Hui. “Synthesis of Discodermolide Subunits by SE2’ Addition of Nonracemic Allenylstannanes to Aldehydes.” Journal of Organic Chemistry 63 (1998): 817-823.
Marshall, James A. Johns, Brian A. “Total Synthesis of (+)-Discodermolide.” Journal of Organic Chemistry 63 (1998): 7885-7892.
Assesment:
We worked on the review completely as a group. The three of us looked for an article. We spent equal amounts of time reviewing the retrosythesis and writing this assignment.