(-)-Mniopetal E
Suzuki, Y, et. al. (2000) “Total Synthesis of (-)-Mniopetal E, a Novel Biologically
Intriguing Drimane Sesquiterpenoid” Journal of Organic Chemistry. 65, 8595-8607.
Reviewed by Carolyn Smith and Kayla Crank
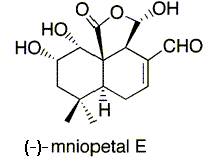
(-)-Mniopetal E is a drimine-type sesquiterpenoid that has the ability to inhibit the RNA directed DNA polymerases (reverse transcriptases) of some RNA viruses such as the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1. Therefore, the ability to chemically synthesize this natural compound is critical in the mass treatment of such viruses.
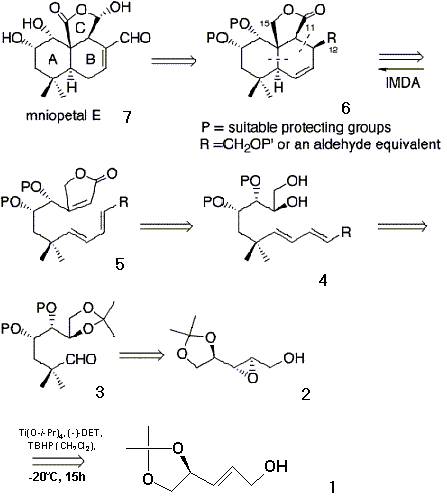
Retrosynthesis reaction of on next page (-)-Mniopetal E
To begin the reaction, (1) D-mannitol [(E)-1,2-(isopropylidenedioxy)-3-penten-5-ol] is reacted with enantiomerically pure (-)-DET (diethyl tartrate) in a sharpless epoxide reaction to produce only the (-) enatiomer of 2. This reaction replaces the double bond on the third carbon with an epoxide below the plane of the compound thus it is a (-) enatiomer. If (+)-DET had been used instead, the epoxide would be above the plane of the compound as a (+) enantiomer. The epoxide group is then opened through a Payne rearrangement to produce 4,5,6,7-tetrahydroxyheptanol (3). The Payne rearrangement proceeds in three steps. First, the (-) enantiomer (2) is reacted with KN(TMS)2 in toluene-THF (in a 6:1 ratio at –78 C) to switch the OH group on the fifth carbon with the epoxide group on the third carbon. Then, through the addition of PhMgBr and 2,2-lithiumcyandinepropane, the epoxide group is broken and 2-cyanidepropane is added to the fifth carbon. Also after the epoxide is broken, the O from the broken epoxide and the O from the OH on the third carbon react with MOMCl (methoxymethyl chloride) and which is shown as the P group in the retrosynthesis reaction starting in compound 3. Then through an SN2 reaction, used to prevent multiple products found with SN1 reactions, the CN group leaves and is replaced with CHO. 1,4-disubstituted butadiene (4) is prepared by reacting 3 with (EtO)2P(O)CH2CO2Et / NaH twice. The first time, it replaces the OH on the sixth carbon with a double bond attached to a CO2Et. The second time, the solution replaces the O2Et on the eighth carbon with another double bond attached to a CO2Et, which is R in the retrosynthesis reactions. 5 is prepared from 4 by introducing the butenolide ring (a four carbon ring resembling THF with a double bonded O attached to the first carbon next to the O in the ring, and a double bond on the second carbon). To do this, the compound is reacted with a variety of solutions which yield many products, finally leading to the intended product, 5. To produce compound 6, a Diels-Alder reaction occurs between the double bond of the butenolide ring and the double bonds on the eigth and tenth carbons of the longest chain. Finally, the natural compound (-)-mniopetal E is produced by adjusting the oxidation states of 6.
Both Kayla and Carolyn worked an equivalent amount on this review. Both of us together looked on the Internet and in the library for a total synthesis of a natural compound. We then met and typed this report together.
Retrosynthetic reaction of (-)-mniopetal E: