In-class notes for 09/23/2020
CS 273 (OS), Fall 2020
HW5, due tonight
Questions on pthreads or text IPC problems?
Threads and P-thread coding
-
Function pointer types
Example:
int add1(int x) { return x+1; }By itself, the C identifieradd1has typeint (*)(int)Example:
void strcopy(char *arr, char *str) { ... }The C identifierstrcopyhas typevoid (*)(char*, char*)
IPC
Two other featured IPC strategies besides semaphores
Monitors - and object-like approach.
(Java does something similar)Message passing - networking approach, usable on distrib systems
Example: Synchronization server
Scheduling
Recall process states:
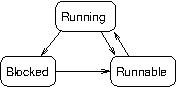
In process management within an OS, scheduling means choosing the next running process among all the runnable processes
Exercise per table: come up with three or more factors or goals a scheduler might consider, then report out. Some examples:
- Fairness
- Response time
- Handle both I/O bound and compute bound processes
Some terms related to scheduling (see text for definitions)
Some algorithms for scheduling
IPC
Thread-safe data structure exercise with Message Passing
Synchronization server's code
int A[MAXARRAY]; REPEAT FOREVER: receive(&any, &msg) // receive msg from any proc; remember that proc if type(msg) == GET_ARRAY retmsg = make_msg(GET_RESPONSE, A[index(msg)]) send(any, retmsg) else if type(msg) == SET_ARRAY A[index(msg)] = val(msg) retmsg = make_msg(OK_MSG) send(any, retmsg) else retmsg = make_msg(INVALID_TYPE_MSG, type(msg)) send(any, retmsg)Client processes' library functions
function get_array(i) msg = make_msg(GET_ARRAY, i) send(sync, msg) receive(sync, &retmsg) return val(retmsg) function set_array(i, val) msg = make_msg(SET_ARRAY, i, val) send(sync, msg) receive(sync, &retmsg)
Producer-consumer problem - a richer problem than the simple thread-safe data structure problem
Needs thread-safety for its buffer data structure (array of items)
Block if necessary for mutual exclusion, as before
But also requires that:
a producer blocks if necessary until a slot becomes available when the buffer is full; and
a consumer blocks if necessary until an item becomes available, when the buffer is empty.
These multiple needs for blocking must be handled with correct IPC.
Solutions to producer-consumer problem using semaphores, monitors, message passing
< >