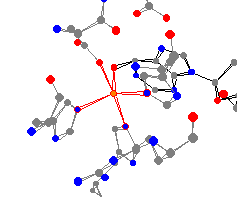
important in immune system maintenance. This enzyme catalyzes the irreversible
deamination of adenosine and 2'-deoxyadenosine. An interesting thing about
this enzyme is that it produces a reaction rate increase on the order of 1012
when compared to the reaction without the enzyme.1 The average axial bond
distance is 214 pm, and the average equatorial bond distance is 226 pm.
Back to Study Introduction Page
Back to Molecular Origami Home Page
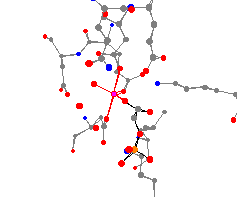
the breakdown of glucose and the formation of ATP and NADH. It catalyzes the elimination of water
from 2-phosphoglyceric acid to make phosphoenolpyruvate, the only dehydration reaction in
glycolysis. Enolase is activated by Mg(II) and Zn(II) and inhibited by phosphoglycolate.2
The average axial bond distance is 213 pm, and the average equatorial bond distance is 195 pm.
Trigonal Pyramidal Zinc
Two Other Zinc Structures